In the experimental group 34 of these patients received in addition to the conventional therapies a treatment with Medical Resonance Therapy Music®, and in the control group 22 patients received the conventional drug treatment only.
In all patients the individual profiles of the functional asymmetry of the brain (IPFA) were documented, which demonstrate the state of coordination of the different hemispheres of the brain and their disbalance.
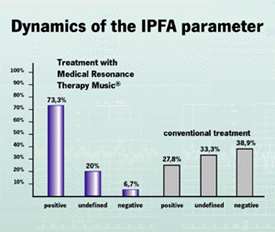
The dynamics of the integral parameter (IPFA) was positive in 73,3% of the patients of this group, in 20% it was undefined and in 6,7% it was negative.
The changes of the IPFA values had differently directed shiftings depending on the initial level, which was determined by the epileptic focus in the brain. Often a tendency towards a reduction of the coefficients of the right ear were observed – a parameter which mirrors the coordination of the hemispheres of the brain and which could demonstrate a predominant effect of this music on the function of the right hemisphere of the brain.
Here the dynamic of the IPFA-values was positive in 27,8% of the patients, undefined in 33,3% and negative in 38,9%.
Investigators:
Dr. med. T. J. Teterkina
Prof. Dr. med. W. Sidorenko
Dr. med. A. S. Fedulow
Dr. med. G. A. Lukaschewitsch
Dr. med. G. W. Massalski